Trading strategies: Speculating, hedging, and spreading in the futures market
by Coinbase Derivatives LLC
In this article we’ll break down the basics of futures so you can start participating in the futures market. Here you’ll get to know three common strategies in futures trading: speculating, hedging, and spreading.
Introduction
Investors can engage with the futures market in a couple different ways, either going long or short a given contract. This flexibility can make futures strategic assets in an investor’s portfolio.
Investors can leverage futures strategically to accomplish a number of goals. Three common strategic approaches in the futures market include speculating, hedging, and spreading.
Speculating on price movements
Speculation involves predicting future price changes and taking positions accordingly. When investors speculate with futures, they aim to profit by going long or short based on their market expectations.
If a speculator believes the price of an asset will increase, they might go long by purchasing a futures contract, intending to sell it at a higher price. Conversely, if they think the price will fall, they might take a short position, selling a futures contract with the plan to repurchase it at a lower price.
In both scenarios, the objective is to anticipate market movements correctly and capture potential profit from price fluctuations.
Hedging to manage risk
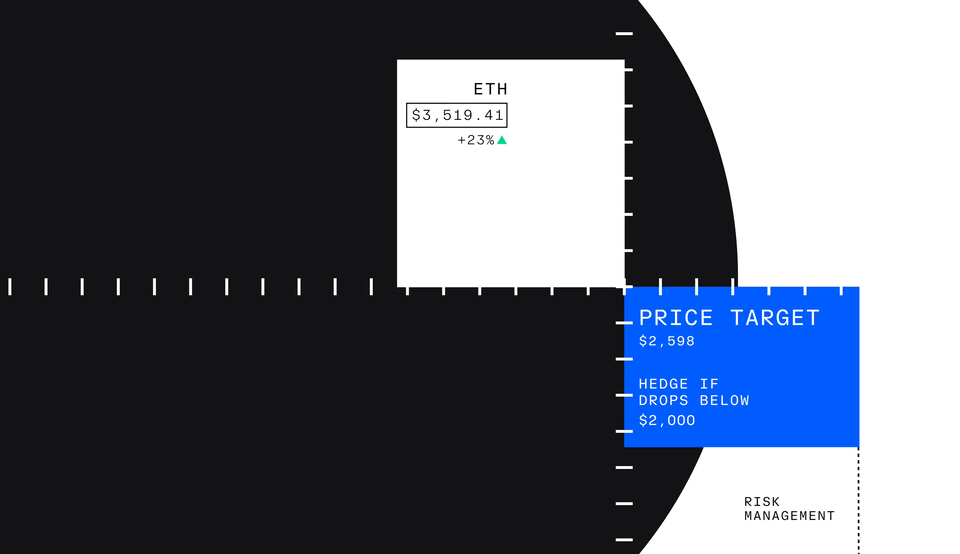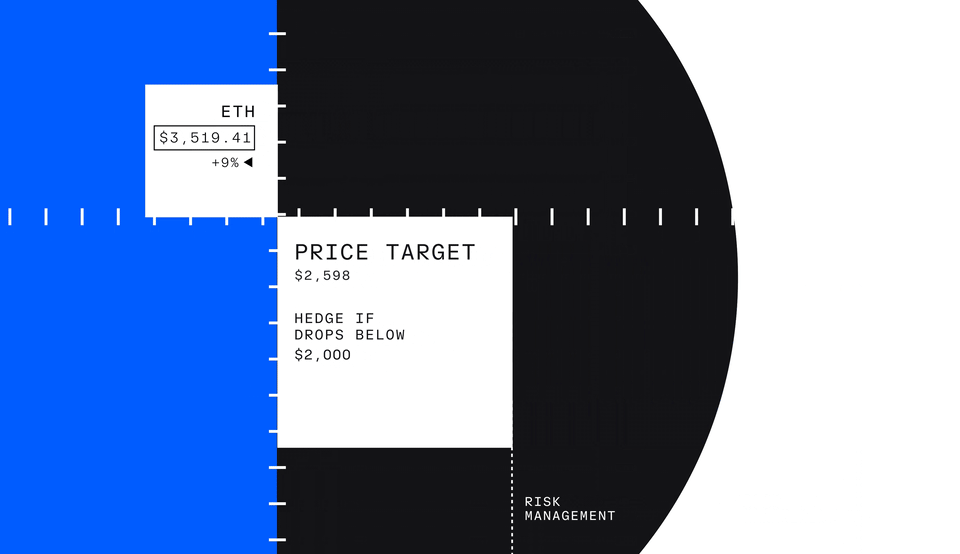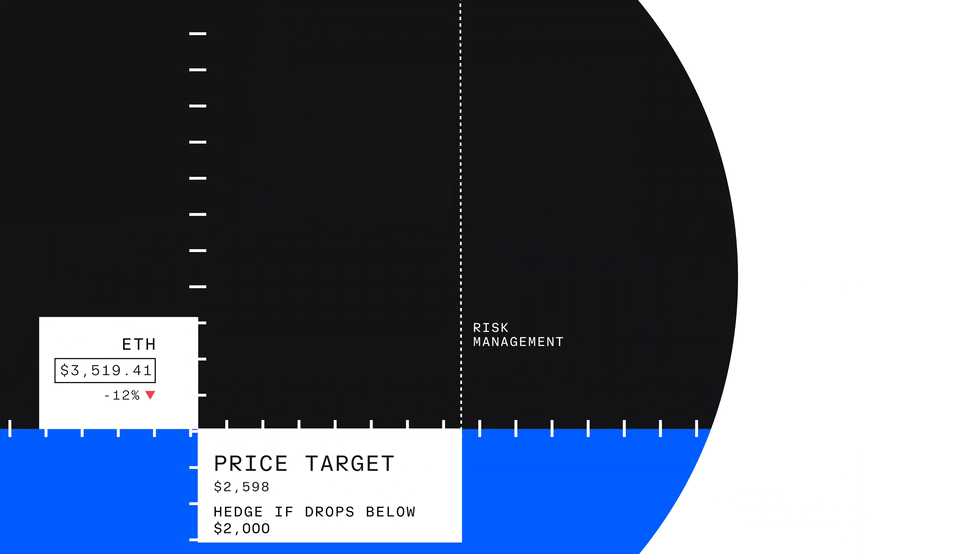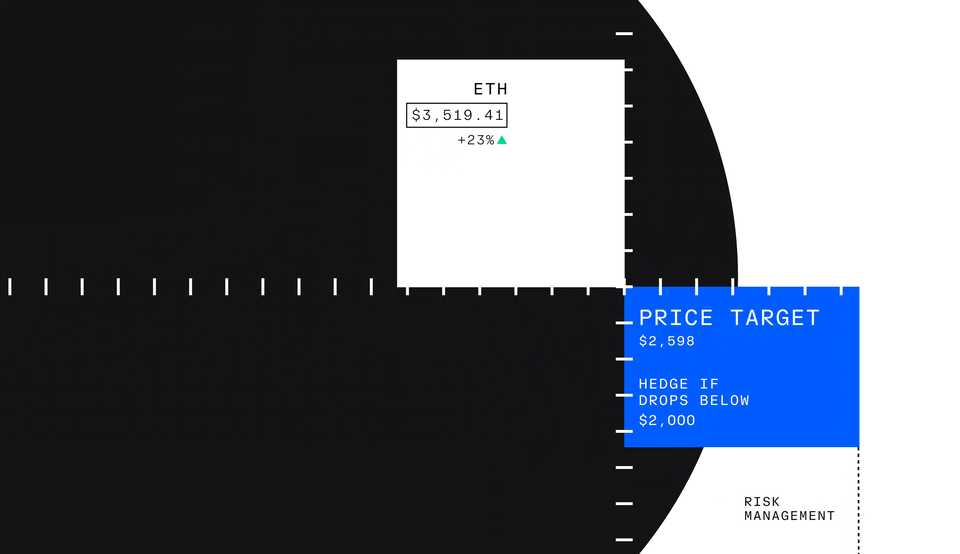
But profit isn’t the only reason investors might trade futures—investors can also use futures to hedge, which means protecting an investment by reducing risk.
Let’s take a look at an example with an investor who owns Ether. If they believe in its long-term value but are concerned about short-term price drops, they might choose to hedge. To do so, they could go short nano Ether futures, selling the contract at the current price with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price if Ether’s value decreases.
The investor has 1 Ether at $4,000. They hedge their investment by going short on 20 nano Ethers futures. Each nano Ether future represents 1/10th of an Ether. Therefore, the notional value of the contracts is 20×400=$8,000.
The contracts have a 30% initial margin requirement, which means that to open the position, the investor is required to deposit $2,400 (30% of $8,000) to control the 20 contracts.
The price of Ether then drops to $2,000, so each nano Ether futures contract’s value drops to $200. That means the value of the 20 contracts is now 20×200=$4,000. To close their position, the investor buys them back at that price.
Since the initial value of the contracts was $8,000 when the investor sold them and is now $4,000, the investor profits $4,000 from their short position.
This profit can offset the losses in the value of the investor’s actual Ether holdings. By using nano Ether futures to hedge, the investor reduces the impact of the price drop on their overall portfolio, allowing them to manage risk more effectively.

Spreading to trade the difference
Spreading is a futures trading strategy where an investor aims to profit from the price difference between two related positions rather than guessing if the market will go up or down. That is, instead of betting on the market’s overall direction, the focus is on how two contracts move in relation to each other. There are different types of spreads used to do this.
Intermarket spread
An intermarket spread involves taking positions in two different but related assets. The goal is to profit from the price difference between the two assets rather than betting solely on the direction of one.
For example, if an investor believes that the price of Bitcoin futures will rise, they might go long Bitcoin futures. To spread and reduce risk, they could simultaneously take a short position in gold futures, expecting gold prices to fall.
If the price of Bitcoin rises and the price of gold falls, the investor will profit. With the spread in place, even if the price of gold rises as well or holds steady, the investor would still profit from the first leg of the spread or potentially minimize losses.

Calendar spread
A calendar spread, also called an “intramarket spread,” is a more advanced trading strategy. In a calendar spread, an investor simultaneously opens one short and one long position on the same asset but with different expiration dates. The goal here is to profit from the price difference between the two contracts over time.
For example, if an investor wanted to execute a calendar spread, they could short a March 2025 Bitcoin futures contract and, at the same time, go long an April 2025 Bitcoin futures contract.
Due to market volatility, the price won’t remain exactly steady. However, if the price is relatively stable, the investor could profit even if there’s a loss on one of the legs of the spread.

Spreading strategies like calendar or intermarket spreads can limit the impact of general market trends by instead honing in on relative price movements. By holding positions in different contracts or assets, investors hedge one contract against another, which can potentially lower the risks associated with sudden market swings. Instead of focusing on the overall direction of the market, they aim to profit from price differences between related assets or contract expirations.
Recap
Key terms
Hedging
Protecting an investment by reducing the risk via an offsetting long or short futures position.
Spreading
Calendar or intramarket spread: Simultaneously opening positions in two futures contracts for the same asset but with different expiration dates with the goal of profiting from the price difference between the two contract expiration dates.
Intermarket spread: Taking positions in two different but related assets with the goal profiting on the price difference between the two assets rather than betting solely on the direction of one.
In the futures market, investors can employ a range of strategies depending on what their goals are. Each can be used to potentially drive profit or manage risk.
Futures are rarely used in isolation but rather as part of a broader investment strategy to potentially increase and protect the health of an investor’s overall portfolio.
The risk of loss in trading futures can be substantial. You should, therefore, carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.











