What is the Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC)?
January 26, 2022
The Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC) allows independent blockchains to directly communicate and trade assets
The Inter‐Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC), an open‐source protocol for relaying messages between independent distributed ledgers, was created to connect independent blockchains to one another.
IBC allows heterogeneous chains to trustlessly communicate with each other and exchange value, particularly tokens, which makes them interoperable.
A key feature of IBC is that the connected blockchains do not need to communicate with each other directly. Instead, they are able to send packets of information via dedicated channels using smart contracts to connect to the chains.
The Tendermint‐based decentralized exchange Osmosis allows token holders to directly benefit from what IBC offers by enabling seamless swaps of tokens from different chains.
It’s no longer unusual to hear people in the crypto ecosystem say "the future is multichain." As our Business Development Manager, Harry Alford, wrote in a recent post, "In Web2, the bigger network wins. In Web3, whoever builds the biggest network together wins." But less common is the understanding that the future is now and the ability to directly connect independent blockchains via the Inter‐Blockchain Communication protocol is driving a new wave of DeFi liquidity — enabling an interconnected network of specialized projects to grow cooperatively by working together.
The Cosmos ecosystem has a vision of creating the "internet of blockchains," or a network of independent chains that can communicate in a decentralized way. To reach this goal, the Inter‐Blockchain Communication protocol (IBC) was created.
By enabling IBC, independently developed blockchains can natively send data (primarily tokens) directly to one another. Most cross‐chain bridges are built by independent third parties and vary drastically on maturity and security depending on which protocols they interact with, thus potentially compromising their security and providing an inconsistent experience. With IBC, the differentiation is that the data is sent via a dedicated channel by a trustless relayer and then authenticated once reaching the destination chain.
IBC launched in March 2021, and as of November 2021 it has been enabled on 22 networks with over 1.5 million transactions currently executed using IBC per month. Token holders typically utilize IBC via the Osmosis network to seamlessly swap or stake the tokens from IBC‐enabled chains. IBC can also be used to build a broad range of cross‐chain applications including cross‐chain smart contracts, messaging, NFT transfers, oracle data feeds, and more.
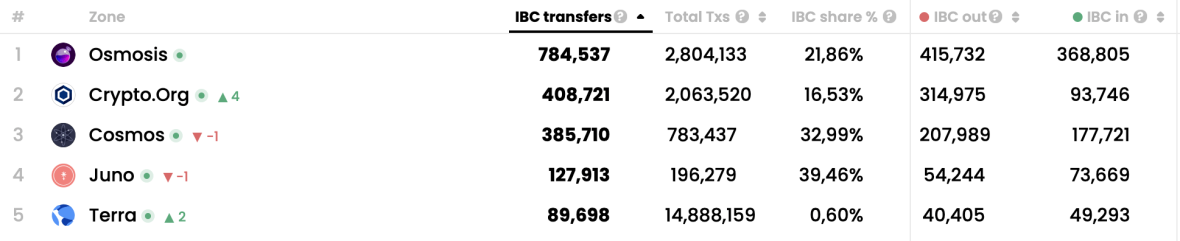
Most active zones by IBC transfers 11/7/21 - 12/7/21 Source
The importance of multichain interoperability
The blockchain industry is experiencing a renaissance of development and community engagement. As more projects, use cases, and innovative deployments enter the space, there is a consistent need for the specialized functionality, or certain scalability, that tailor‐made networks can provide.
It’s commonly understood that the value of a system is greater than the sum of its parts. For example, in the case of sovereign nations, each country can feasibly provide for its residents on its own, but may have surpluses of one resource or not enough of another. A global trade network provides more value than the sum of its international parts, with the ability to easily trade surpluses of necessary goods providing more value to citizens than the creation of those goods on their own. Blockchains are no different in this sense, and interoperability between chains with distinct use cases can drive a greater utility than the sum of their parts.
One example of the larger benefit of this shared interoperability is superfluid staking using IBC, a feature that will in the future be enabled on Osmosis. Using Osmosis as the user interface, token holders will be able to deposit any two participating networks’ supported tokens into an Osmosis liquidity pool, and can then stake their liquidity shares to validators on the tokens' home chains.
In doing so the deposited asset will not only earn its share of fees from the liquidity pool’s swap transactions, but will also earn rewards from helping secure the chain, allowing users to simultaneously provide liquidity to the Osmosis AMM and still participate in the native ecosystems of the tokens they hold by staking. For example, an OSMO<>AKT pool’s LP tokens will be able to secure the network and earn staking rewards on both the Osmosis and Akash networks. This aligns the incentives of both those interested in governance and security of the chain with those that are looking for opportunities to generate high rewards.
This is important in part because a blockchain networks’ security is proportional to the amount of value locked in them. However, because most independent blockchains are not yet fully interoperable, users frequently choose to exchange or swap their tokens, leaving one blockchain ecosystem to explore opportunities in another, or choosing to invest in higher‐yield opportunities instead of participating in securing a network directly via staking. This allows users to not have to choose between earning liquidity rewards and actively participating in the networks whose values and functions they want to help secure.
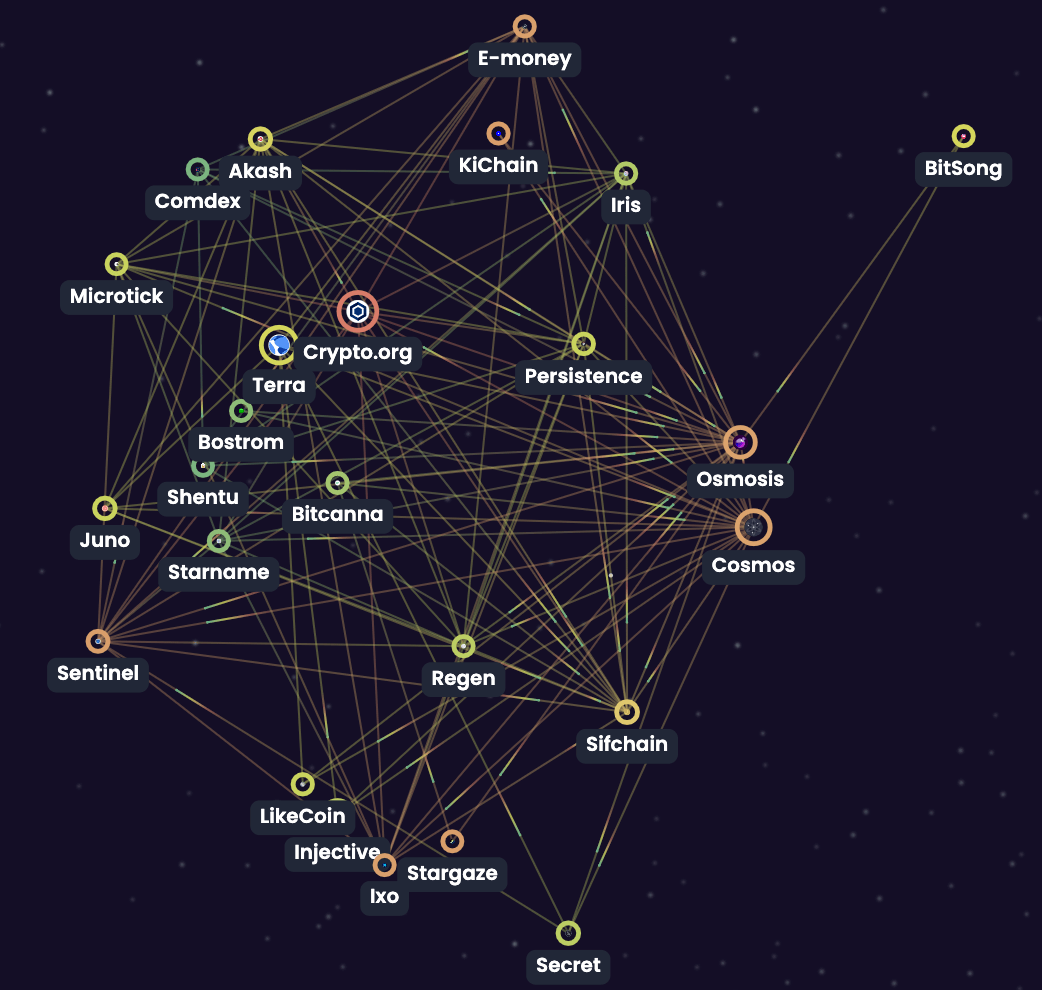
Visual of interchain channels and live IBC transfers from Map of Zones
How IBC works
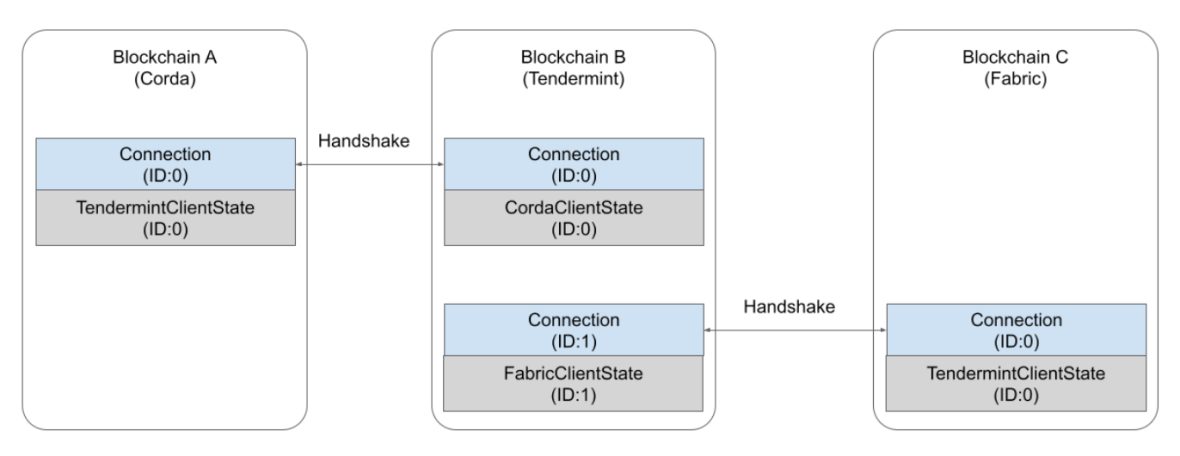
IBC is a protocol for allowing independent blockchains to trustlessly communicate with each other. While IBC is a core piece of Cosmos’ roadmap and as such is now primarily used by blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem, any blockchain can connect and communicate to others using IBC in its standardized form, the Inter‐Chain Standard (ICS).
IBC consists of two layers: the base‐level TAO (transport, authentication, and ordering) layer, and the APP (application) layer, built on top of TAO. While the TAO layer is primarily responsible for the functionality of IBC, any application‐layer protocol can be built to operate on top of it.
A key feature of IBC is that the connected blockchains do not need to communicate with each other directly. Instead, they are able to send packets of information via dedicated channels, which use smart contract modules that include a light client for trustlessly verifying that the state sent by the other blockchain is valid. The trustless and permissionless nature of IBC means that any party can operate a relayer and the participating blockchains do not need to trust the parties that transfer the information. This is an essential component needed to achieve blockchain sovereignty without isolation — a key objective of the Cosmos ecosystem.
IBC/TAO functions via smart contracts employed on each of the chains, and connected via IBC. Information is sent between the chains as data packets via a permissionless relay layer. The packets are delivered to the destination chain one time, in the same order in which they were sent. The relayer feeds the output of a smart contract from the sender's TAO module to the TAO module on the receiving blockchain, with the help of connection and channel abstraction. Authentication of the received data is handled by an on‐chain light client which verifies that the presented states actually exist on the sending blockchain directly.
Relayers transfer data packets from one smart contract to another via a specified channel
Channels are dedicated with one smart contract connection at each end, so a data packet being sent via a channel proves that the data was sent from that specific smart contract affiliated with the blockchain sender
IBC/TAO modules contain smart contracts which are implemented on each of the blockchains for each channel to facilitate the order of operations
Each IBC/TAO module uses channel and connection abstractions to define and connect the channel’s two smart contracts along with an on‐chain light client to trustlessly verify that the state sent by the blockchain actually exists
How do I use the IBC?
For most individual uses, such as swapping, staking, and providing liquidity with the tokens of IBC‐enabled chains, the Osmosis protocol’s decentralized exchange will be the most direct use of the IBC. It is also possible to complete IBC transfers manually (as was done pre‐Osmosis‐launch) by using the Keplr wallet and selecting the channels to transfer assets between. The fees for conducting IBC transactions are set by each individual blockchain’s parameters, but are currently either very low or entirely free.
Developers who want to build using IBC can find the full IBC implementations and developer documentation in the protocol’s website. The public GitHub repository for the development and documentation of IBC is also open for contributions here. Those building applications that interact with IBC can use our Query & Transact secure read/write infrastructure to easily access blockchain data and build robust applications on 30 protocols, including IBC‐enabled Cosmos, Crypto.org Chain, and Terra.
IBC has opened up a world of interoperability for chains in the Cosmos ecosystem, and the best way to get involved is to take part in the growing Cosmos ecosystem. Learn more about how some of these IBC‐enabled chains work, what their goals are, and how to participate, in our Guide to Cosmos, Guide to Osmosis, Guide to Crypto.org Chain, or Guide to Terra.